The arrival of Europeans in India
- The Europeans were willing to find an alternate route to Asia bypassing the Red Sea region in order to access the Indian subcontinent.
Old World vs New World
Old World- Asia, Africa, and Europe are collectively known as the Old World or Afro-Eurasia.
New World- After the beginning of the Age of Discovery, new lands comprised the Americas and its nearby islands (Oceania), collectively known as the New World.
- In this scenario, the two Iberian powers, Spain and Portugal embarked on the maritime journey to begin what is known as the Age of Discovery followed by other European powers such as the Italians, the Dutch, the English, the Danes, the Swedish and the French.
- Henry – the Navigator, prince of Portugal initiated the first great enterprise of the Age of Discovery-search for a sea route to the east.
- In 1494, the kingdoms of Spain and Portugal signed the Treaty of Tordesillas.
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) Under this treaty Spain and Portugal divided the non-Christian world between them by considering the Atlantic as an imaginary line. The rulers of Portugal could claim anything to the east of this line and the rulers of Spain could claim anything to the west of it.
- Gradually, these European companies began to consolidate their position in India by building factories, sometimes by fortifying them in order to protect them from other European powers.
Factories: A Factory was a warehouse to store things. No manufacturing activity used to take place in them (unlike the present sense of a factory).
Ferdinand Magellan: He became the first European to cross the Pacific Ocean by circumnavigating the Earth.
Feitorias: It was an unfortified trading post on a strategic location set up by the Portuguese. Feitorias means factory on land.
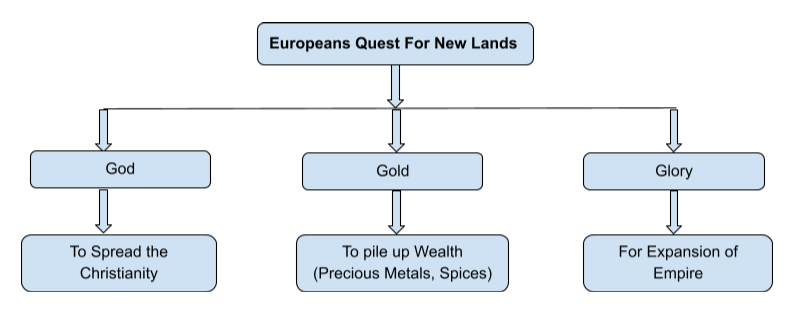
Causes of the Age of Exploration
- For the promotion of Christianity in Non – the Christian World (God)
- To expand the territories of their respective empires (Glory)
- To earn commercial gains in the East Indies through the trade of various commodities including silk, gems, precious metals & spices (Gold)
- To test their ability in the field of maritime navigation and shipbuilding
- To find the alternate sea route to Asia than the Red sea route since Ottoman Turks blocked the land routed
- To establish hegemony on newly colonized land by defeating other European Rivals (Imperialism).
- To undertake new discoveries out of curiosity since the Europeans were filled with Renaissance spirit during this time.
1st Factory of European Companies in India
| S.No. | European Company | Location | Year of Establishment |
| 1. | Portuguese | Calicut (Kerala) | 1503 |
| 2. | Dutch | Masulipatnam (Andhra Pradesh) | 1605 |
| 3. | English | Surat (Gujarat) | 1608 |
| 4. | Danes | Tranquebar (Tamil Nadu) | 1616 |
| 5. | French | Surat (Gujarat) | 1668 |
The Portuguese
Bartolomeu Diaz (1450-1500)
- Bartolomeu Diaz was the first European to sail around the Cape of Good Hope rounding the coast of West Africa in 1487. He also found that India was reachable by sailing around the coast of the continent.
- In 1542, St. Xavier led the conversion of the Paravars (Fisherman tribe on the Coromandel coast) and Mukkuvars (Malabar coast) into Christianity.
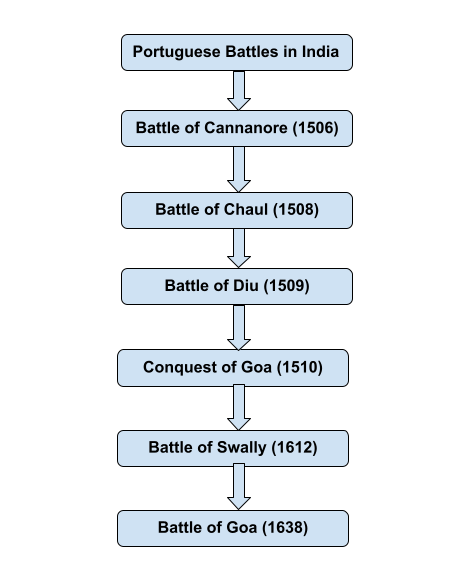
- The Portuguese lost Surat to the English in the Battle of Swally Hole 1612.
- The Dutch acquired all Portuguese settlements located on the Malabar coast by 1663.
- The Portuguese had lost all possessions in India by the end of the 17 century except Goa, Daman and Diu, since the Marathas captured Salsatte and Bassein from the Portuguese in a battle known as the Battle of Vasai (Bassein) in 1739.
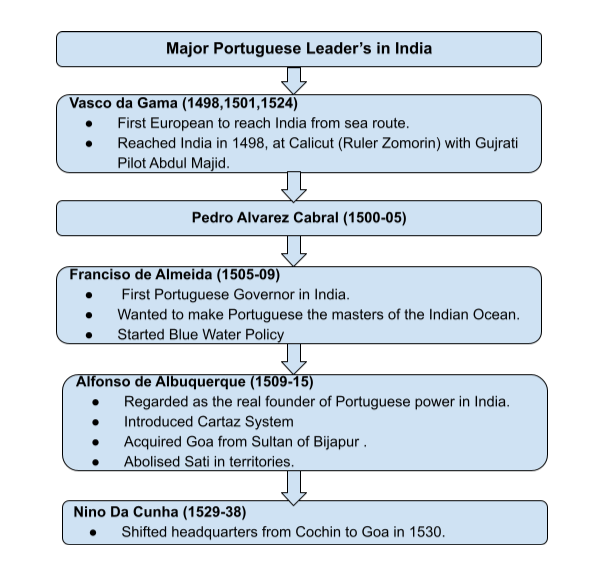
Blue Water Policy He believed that, instead of building factories and fortresses on land, they should emphasize on becoming powerful at the sea in order to check Arab invasions along with the other rival European companies.
Cartaz SystemIt was a system of granting a license or pass through which the Portuguese forced all the merchant ships to buy a license on passing through their territories. Otherwise, ships and goods were confiscated.
Contributions of the Portuguese
- The cultivation of Tobacco and Potato, Pineapple, Chilies, Tomato and also they introduced crops like Cashew nuts and better varieties of Coconut.
- The first Printing Press in 1556 at Goa.
- The first scientific work on Indian medicinal plants.
- The arrival of the Portuguese marked the emergence of Maritime power in Europe.
The Dutch
- The United East India Company of the Netherlands or the Verehgidge Oost Indische Compagnie (VOC) of the Netherlands was formed in 1602.
- It was the first multinational corporation in the world and also was the first company to issue stocks.
- Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutchman to reach Sumatra and Bantam in 1596.
- The first Dutch factory was established at Masulipatnam in the Andhra region in 1605.
- The greatest Dutch merchant to visit India was Jan Hughen Van Linshotten.
- He wrote Itinerario, a detailed account of India. Later, in his honour the Dutch East India Company popularly came to be known as Jan or Van Company.
- The Dutch were able to overpower the Portuguese in India.
Establishment of Dutch Factories
| Location | Year |
| Masulipatnam | 1605 |
| Pulicat | 1610 |
| Surat | 1616 |
| Chinsurah | 1653 |
| Kasimbazar, Balasore, Patna and Nagapatnam | 1659 |
| Cochin | 1663 |
- The Dutch even acquired Ceylon (Sri Lanka) from the English.
- The English defeated the Dutch in the Battle of Bedara/ Chinsura/Hooghly in 1759. This strengthened the position of the English in Bengal.
- Dutch presence in the Indian subcontinent lasted from 1605-1825.
- Subsequently, the Dutch established their monopoly over the Malaya Peninsula as well as on the Indonesian archipelago which they acquired after defeating the Portuguese.
The English
- On 31″ December 1600 Queen Elizabeth I issued a Royal Charter by which a Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East Indies was constituted.
- This company decided to establish a factory at Surat in 1608 on the western coast of India.
- For this purpose, Captain William Hawkins was sent by James I (King of England) to the Mughal court to get permission from emperor Jahangir in 1608. However, he did not succeed due to the opposition from the Portuguese.
Ralph Fitch was the first English merchant to visit the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar at Fatehpur Sikri in 1585.
Captain William Hawkins sailed to India from a ship named Hector. He was the first English who came to India via the sea route.
- In November 1612, the English Commander Captain Thomas Best sailed to India from a ship named Dragon and a small ship Osiander. In 1612, the Battle of Swally (Suvali in Surat) was fought between the company forces and the Portuguese.
- Mughal emperor Jahangir issued a Farman permitting the company to build a factory at Surat.
The First English factory was set up in Masulipatnam (Andhra Region) in 1611 after getting permission from the ruler of Golconda.
Farman
A Farman was an irrevocable royal order issued by the Mughal authority i.e. King or Emperor.
- In 1615, Sir Thomas Roe succeeded in getting permission from Jahangir to build factories at Agra, Ahmedabad, and Bharuch.
- In 1662, Charles II, the King of England received the island of Bombay in dowry by the King of Portugal when the former married the Portuguese Princess Catherine.
- Their position was further strengthened, when the English received a Golden Farman from the Sultan of Golconda in 1632 which permitted a duty-free trade in the port of Golconda for an annual payment of 500 Pagodas.
- Gerald Aungier is often considered as the real founder of Bombay in 1669.
- The company constituted a committee known as the Court of Directors with the purpose of carrying out administrative functions smoothly.
Gerald Aungier is often considered as the real founder of Bombay in 1669.
- The company constituted a committee known as the Court of Directors with the purpose of carrying out administrative functions smoothly.
The Court of Directors had 24 members (directors), who worked as clerks, writers, and service providers were known as the factors.
- Shah Shuja, Subedar of Bengal, issued a Farman granting certain trade privileges to the English in Bengal.
- The East India Company interpreted the Farman according to its own interests and started building a fortified settlement instead of a factory.
- This fortified settlement in Bengal came to be known as Fort William which was established in 1700.
- It became the seat of the Eastern Presidency and Charles Eyre was appointed as its first president. Fort William served as the capital of the English power in India till 1911.
Norris Mission
William III, the King of England, constituted a company in 1688, which became famous by the name of English Company Trading in the East.
Foundation of Calcutta
Job Charnock was the founder of Calcutta (1698) after British acquired the Zamindari of three villages suttanati, kalikata and Govindpur.
The Danes (Danish)
- The Danes came from Denmark to India in 1616.
- They established their first factory at Tranquebar (Tharangambadi, Tamil Nadu) in 1620.
- The Danes built their second factory at Serampore (Bengal) in 1676 and made it their
- headquarters.
- The Danes sold all their factories to the English and left India in 1845. They were more concerned with missionary activities.
The French
- Under Louis XIV, a French company named Compagnie des Indes Orientales was formed in 1664.
- This French Company was totally controlled and regulated by the French government.
- The first French factory at Surat was established by Francois Caron in 1668 and the second factory was established by a Persian Mercara at Masulipatnam in 1669.
- In 1674, Francois Martin became the first French Governor-General of Pondicherry.
Francois Martin founded the city of Pondicherry in 1668. Later on, it became the capital of the Portuguese in India.
- The Dutch (in alliance with the British) captured Pondicherry in 1693. But the Treaty of Ryswick restored Pondicherry to the French.
- Saishta Khan, the Subedar of Bengal allowed the French to build a factory near Chandernagore in 1674.
- The French acquired and controlled Mauritius in 1721, Mahe (Malabar coast) in 1725, and Karaikal in 1738.
- The French governor Joseph Francois Dupleix captured Madras in 1746, which was restored to the English in 1748.
Joseph Francois Dupleix was the first European who initiated the policy of intervening in the internal matters of the princely states.
- In order to control the southern regions of India, the French and English fought three major wars known as the Carnatic Wars between 1746 and 1763.
- Ultimately, the English defeated the French leading to the gradual decline of the French power in India.
Reasons of English Success
- Structure and nature of trading company-mostly private shareholding and less state-controlled.
- The industrial revolution in England gave a boost to the British economy.
- Well-trained, skilled, and highly disciplined military.
- Stable government with efficient monarchs (Except Glorious Revolution, 1688).
- Lesser Zeal for religion and less interest in spreading Christianity.
- Britishers used the Debt market to fund its wars.
- Naval superiority.

