1. Nuclear Energy for Net Zero Viksit Bharat – Challenges and Strategic Roadmap – Science and Technology

Why in News?
India is pursuing the ambitious twin goals of:
- becoming a developed nation (Viksit Bharat) by 2047, and
- achieving net zero carbon emissions by 2070.
To meet these goals, India must significantly increase its clean energy capacity. Nuclear energy is expected to play a pivotal role, with a projected contribution of nearly 20,000 TWh to India’s energy mix.
Key Points
1. India’s Energy Transition Goals
- Net Zero Target: 2070
- HDI Goal: 0.95 (currently ~0.633 as per UNDP)
- Current Energy Consumption: ~9,800 TWh (majorly fossil fuel-based)
- Projected Clean Energy Requirement: ~2800 TWh annually
- Role of Nuclear: Major contributor (~20,000 TWh total contribution over time)
2. Importance of Nuclear Energy
- Low-carbon, reliable base-load energy source
- Enhances energy security and sustainability
- Critical to balancing development with environmental goals
India’s Nuclear Energy Program
A. Three-Stage Nuclear Power Programme
Envisioned by Homi Bhabha
| Stage | Technology | Fuel | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) | Natural Uranium | Dependence on imported uranium |
| 2nd | Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) | Plutonium | Slow progress, limited operational capacity |
| 3rd | Thorium-based Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs) | Thorium | Underdevelopment, need for advanced R&D |
B. Current Domestic Capabilities
- PHWRs remain central to India’s nuclear fleet
- Light Water Reactors (LWRs) supplement PHWRs
- 100 GWe Mission by 2047: Aims to dramatically scale up nuclear capacity
C. Fuel Supply and Security
- Projected uranium requirement for 100 GWe: ~20,000 tons/year
- Necessitates:
- Fuel recycling technologies (e.g., reprocessing spent fuel)
- Reduced dependence on imports
- Strategic international partnerships for secure supply chains
Conclusion
By strategically advancing its indigenous nuclear program, particularly through PHWRs, FBRs, and Thorium technologies, India can:
- Achieve clean energy targets
- Enhance energy security
- Position itself as a global leader in sustainable nuclear innovation.
A self-reliant, secure, and scalable nuclear energy framework will be essential for achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- Consider the following statements regarding India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Power Programme:
1. Stage 2 involves the use of Thorium in Fast Breeder Reactors.
2. Stage 3 is based on the use of Plutonium-based fuels.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D. Neither 1 nor 2 - Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), recently seen in news, are related to:
A. Solar Power Generation
B. Biofuel Production
C. Hydrogen Fuel Production
D. Nuclear Power Generation
Answer: D. Nuclear Power Generation
Mains
1. Discuss the strategic role of nuclear energy in helping India achieve its clean energy and development goals under the Viksit Bharat initiative. What challenges does the Indian nuclear energy sector face in this regard?
2. “India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Power Programme holds the key to its long-term energy security.” Critically examine this statement in light of India’s net-zero targets.
2. Significance of the Next Census for India’s Economy – Economy

Why in News?
- The Government of India will conduct the next Census in 2026-2027, with March 1, 2027 as the reference date.
- The last Census (2021) was postponed due to the Covid-19 pandemic, marking the first major delay since India’s decadal Census tradition began in 1881.
- The delay (6 years) is longer than in neighboring countries (Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka).
- The delay was partly due to reliance on ~30 lakh primary school teachers as Census enumerators, who could not be released without affecting education.
Key Points
1. Why is the Census Important?
- Foundational for Economic Planning and evidence-based governance.
- No effective substitute in terms of data accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- It is the baseline for almost all subsequent official surveys.
2. Economic Significance of Census Data
| Area | How Census Data Helps |
|---|---|
| Inflation control & interest rates | Used by RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee to analyze Consumer Price Index (CPI) trends. |
| Migration patterns | Essential for understanding internal migration, crucial for labor markets, housing, infrastructure. |
| Urbanization | Informs urban planning—critical as Indian cities contribute significantly to GDP. |
| Welfare schemes | Ensures accurate targeting of subsidies, healthcare, education, food security. |
| Fiscal policy | Supports state-level fiscal planning and resource allocation based on updated population data. |
3. Comprehensive Data Coverage
- Demographics: Age, gender, household size, etc.
- Economic status: Employment, income.
- Education levels.
- Migration trends.
- Disabilities.
- Language diversity.
4. Why the New Census is Urgently Needed
- Migration data is currently based on the outdated 2011 Census, causing policy distortions.
- Uncertainty about urbanization rate affects effective urban governance:
- Urban infrastructure
- Transport systems
- Housing policies
- Environmental planning
- Accurate population data is vital for tracking India’s demographic dividend and planning for future needs (health, education, jobs).
Conclusion
The upcoming 2026-27 Census is critical not only for economic planning but also for understanding India’s rapidly evolving demographic and social dynamics.
Timely and accurate data will help policymakers design more responsive and effective programs, ensuring that India’s developmental trajectory remains inclusive and sustainable.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- Which of the following areas are directly informed by Census data in India?
1. Interest rate decisions by the RBI
2. Urban planning and infrastructure development
3.Migration and labour market analysis
4. Defence policy formulationSelect the correct answer:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1 and 4 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: A. 1, 2 and 3 only - The first decadal Census in India was conducted in:
A.1871
B. 1881
C.1891
D. 1901
Answer: B. 1881
Mains
1. Examine the economic significance of the decadal Census in India. How does accurate Census data contribute to sound macroeconomic and fiscal policy formulation?
2. The delay in India’s decadal Census poses several challenges for governance and planning. Discuss these challenges, particularly in the context of urbanization and internal migration.
3. Why Governments Revise GDP Base Year and Methodology – Economy

Significance of the Proposed 2026 Revision for India
Why in News?
- India will update the GDP base year to 2022-23, with revised data expected by February 2026.
- The decision was confirmed by the Ministry of Statistics.
- The aim is to improve the accuracy, reliability, and international compatibility of India’s economic data.
- This revision is particularly important as India’s economy has undergone major structural changes in recent years.
Key Points
1. What is the GDP Base Year?
- The base year is the year against which real GDP (GDP adjusted for inflation) is measured.
- GDP calculations are periodically revised to reflect:
- structural changes in the economy
- updated prices
- new data sources
2. Why Revise the Base Year?
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reflect structural changes | India’s economy has shifted from agriculture to services, digital platforms, and the gig economy. A new base year captures these changes better. |
| Update data sources | Incorporation of new datasets such as Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) and MCA-21 (corporate data) provides better coverage and accuracy. |
| Align with international standards | Ensures compliance with UN and IMF guidelines, enabling more credible real GDP comparisons globally. |
| Address inflation distortions | Updated base year corrects for outdated price structures that can distort real growth figures. |
3. Structural Changes Since Last Revision
- Increased digitalization and rise of e-commerce and gig economy.
- Expansion of financial services, startups, and technology sectors.
- Greater formalization of the economy post GST and demonetization.
4. Importance of Improved Data Sources
| Data Source | Role in GDP Calculation |
|---|---|
| PLFS | Provides better and timely data on employment and labor market trends. |
| MCA-21 | Offers updated corporate sector data for national accounts. |
| Administrative records | Enhance reliability and coverage of GDP data. |
5. Challenges in Previous Revisions
- The 2017-18 base year revision was delayed due to:
- Poor data quality in the Consumer Expenditure Survey (CES).
- Economic disruptions caused by demonetization and GST rollout.
- Concerns that 2017-18 was an unstable year, unsuitable as a reference.
Conclusion
The upcoming GDP base year revision is a crucial reform that reflects India’s dynamic and evolving economy.
By incorporating new data, addressing past challenges, and aligning with global standards, it will strengthen the foundation of economic decision-making and enhance India’s global economic image.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), used in GDP base year revisions, provides data on:
A. Health indicators
B. Consumer price trends
C. Labor market and employment trends
D. Banking and financial transactions
Answer: C. Labor market and employment trends - The MCA-21 database is maintained by which of the following ministries?
A. Ministry of Finance
B. Ministry of Labour and Employment
C. Ministry of Corporate Affairs
D. Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
Answer: C. Ministry of Corporate Affairs
Mains
1. Why do governments periodically revise the GDP base year and methodology? Explain the significance of the proposed 2026 revision for India’s economic data credibility and policy-making.
2. Discuss the role of improved data sources, such as the PLFS and MCA-21, in enhancing the quality and accuracy of India’s national accounts statistics.
4. Drone Warfare & India – Defence & Security

Why in News?
- Former Army Chief Gen. M M Naravane (2021) warned about the growing risks of low-tech asymmetric warfare.
- Recent incidents have highlighted the threat of drone warfare:
- Ukraine used cheap FPV drones to attack 5 Russian airbases, bypassing conventional air defenses.
- Pakistan, after Operation Sindoor, launched drone swarm attacks on India, underlining the urgency of upgrading India’s air defense capabilities.
Key Points
1. Rise of Drone Warfare
- Drones or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have evolved since WWII and the Korean War.
- Now widely used in:
- Surveillance
- Reconnaissance
- Targeted strikes
- Swarm attacks
2. Drone Swarms – The New Threat
| Characteristic | Tactical Advantage |
|---|---|
| Collective behavior | Swarms can coordinate in real time and adapt to losses. |
| Saturation attacks | Overwhelm enemy defenses by sheer numbers. |
| Real-time intelligence | Provide continuous ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance). |
| High-value target strikes | Precision targeting with low-cost platforms. |
Global Market Outlook
- Global military drone market:
- $14.14 billion (2023) → projected to reach $47.16 billion (2032).
- Reflects:
- Rising military reliance on unmanned, AI-driven systems.
- Increasing adoption of cost-effective asymmetric warfare tools.
India’s Unique Vulnerabilities
- Porous borders (with Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar).
- Vast diverse population centers and critical infrastructure.
- Risk of surprise drone attacks (both state-sponsored and non-state actors).
Countering Drone Threats
Detection Systems
| Technology | Role |
|---|---|
| AESA radars | Advanced radar for drone detection. |
| Electro-optical & infrared sensors | Detect stealthy, low-signature drones. |
| AI-powered sensor fusion | Integrates multi-sensor data for accurate detection. |
Emerging Technologies
| Solution | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) | Use lasers to disable/neutralize drones. |
| Electronic Warfare (EW) | Jam or spoof drone communication/navigation. |
| Interceptor drones | Capture or destroy enemy drones mid-air. |
Layered Defence Model
- Multi-layered approach combining:
- Early detection
- EW & DEWs
- Interceptor systems
- Kinetic defense (guns/missiles)
- Ensures redundancy, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility.
India’s Anti-Drone Capabilities
| System | Features |
|---|---|
| Akashteer Air Defence Control System | Integrates detection & engagement across the battlefield. |
| DRDO’s Anti-Drone System | Detects, jams, and destroys drones using laser DEWs. |
Conclusion
- Drone warfare marks a strategic shift in modern combat.
- Drones offer asymmetric advantages: low cost, ease of deployment, adaptability.
- India must rapidly:
- Develop resilient and integrated defense systems.
- Collaborate internationally on anti-drone technologies.
- Strengthen domestic R&D to counter evolving drone threats.
The future of warfare will increasingly involve AI-driven, unmanned systems, making it imperative for India to stay ahead in this technological arms race.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs), used to counter drones, typically employ:
A. High-velocity kinetic projectiles
B.Electromagnetic pulses
C. Laser beams or microwaves
D. Chemical explosives
Answer: C. Laser beams or microwaves - The Akashteer Air Defence Control System is developed by:
A. Indian Army
B. Indian Air Force
C. DRDO
D. ISRO
Answer: C. DRDO
Mains
1. Examine the emerging threat of drone warfare to India’s security architecture. Discuss the technological and strategic responses required to counter this evolving challenge.
2. What are the advantages and vulnerabilities of drone swarms in modern warfare? Suggest a comprehensive strategy for India to strengthen its defenses against drone-based attacks.
5. SEBI Launches Verified UPI IDs to Curb Market Frauds and Enhance Investor Protection – Economy

Why in News?
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is introducing a validated UPI handle system for investor-facing intermediaries.
- The goal is to enhance payment security and reduce the risk of fraud in the securities market.
- SEBI is also launching a mobile app (“SEBI Check”) to enable investors to verify UPI IDs.
Key Points
1. What is Changing?
| Current Situation | New Initiative |
|---|---|
| UPI transactions in the securities market use diverse, unverified handles. | Verified UPI handles ending in “@valid” will now be mandatory for all registered intermediaries. |
| No unified verification method for investors. | SEBI Check app will help investors verify UPI handles and related information. |
| No visual confirmation during UPI payments. | Transactions will display a green triangle with a thumbs-up icon to confirm verified handles. |
Timeline
- Transition period: Until December 11, 2026 for existing UPI handles to migrate to the new format.
- Mandatory after 2026: All intermediaries must use verified handles.
Additional Details
UPI Verification Framework
- Applies to all market-facing intermediaries:
- Brokers
- Investment advisors
- Portfolio managers
- Mutual fund distributors, etc.
Visual Confirmation
- Helps users with language barriers or limited digital literacy.
- Increases transparency and trust in payment processes.
SEBI Check App
- Functions:
- Verify UPI ID ownership.
- Cross-check account holder name, IFSC code, and more.
- Verification via:
- QR code scan
- Manual entry of UPI ID.
Rationale for the Changes
- Combatting impersonation scams.
- Addressing increasing cases of digital payment fraud in financial markets.
- Aligning Indian financial market standards with global best practices for digital transaction verification.
Future Outlook
- SEBI’s framework may become a model for secure digital transactions across:
- Banking
- Insurance
- E-commerce
- Other financial sectors.
- Likely to boost investor confidence in using digital payment platforms for securities market transactions.
Conclusion
SEBI’s new UPI verification framework:
- Strengthens investor protection.
- Sets clearer transaction standards.
- Empowers investors through verification tools.
- Positions India’s financial markets as a safer and more transparent digital environment, in line with international norms.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- The SEBI Check mobile application is primarily designed to:
A. Track stock prices in real time
B.Verify UPI handles of intermediaries
C. Provide mutual fund portfolio analytics
D. Enable algorithmic trading by retail investors
Answer: B. Verify UPI handles of intermediaries - Under SEBI’s new framework, verified UPI handles used by intermediaries must:
A. End with “@upi”
B. End with “@valid”
C. Begin with “INV_”
D. Contain a SEBI registration number
Answer: B. End with “@valid”
Mains
1. How do SEBI’s new measures regarding verified UPI handles enhance investor protection and financial market transparency? Discuss the significance of such regulatory interventions in India’s evolving FinTech landscape.
2. Digital financial markets are vulnerable to impersonation scams and payment frauds. Suggest measures that regulators like SEBI can adopt to improve transaction security in the Indian securities market.
6. UN High Seas Treaty – International Relations

Why in News?
- India is unlikely to ratify the UN High Seas Treaty at the ongoing UN Ocean Conference in France.
- This decision comes despite pressure from the host nation and international stakeholders.
- The treaty is seen as a major global effort to protect marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction (BBNJ).
Key Points
1. What is the UN High Seas Treaty?
- Also called the Agreement on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ).
- First legally binding international instrument specifically targeting:
- Conservation
- Sustainable use of marine biodiversity beyond national waters.
- Builds upon the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which first defined the concept of the high seas.
2. Scope of the Treaty
| Parameter | Scope |
|---|---|
| High seas coverage | ~two-thirds of global ocean area (~half of Earth’s surface). |
| Jurisdiction | International waters beyond the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of any country. |
| Gap addressed | Lack of binding international law governing biodiversity conservation in high seas. |
3. Objectives of the Treaty
- Establish a legal framework for:
- Conservation of marine biodiversity.
- Sustainable use of marine genetic resources.
- Addressing regulatory gaps in existing international law.
- Promoting global cooperation and capacity building.
4. Key Provisions
| Provision | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) | Enable creation and management of MPAs in high seas to protect sensitive ecosystems. |
| Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) | Mandate EIAs for activities likely to affect marine environments, even in international waters. |
| Marine Genetic Resources (MGRs) | Ensure equitable sharing of benefits from MGRs, including digital sequence data. |
| Capacity Building & Technology Transfer | Assist developing nations in marine conservation technologies and practices. |
5. Significance of the Treaty
- Fills a major gap in ocean governance.
- Critical for:
- Mitigating biodiversity loss.
- Addressing climate change impacts on marine ecosystems.
- Promoting fair access to genetic resources.
- Aligns with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14: Life Below Water.
6. India’s Position
- India is unlikely to ratify the treaty at present, citing concerns related to:
- Equity in benefit-sharing of MGRs.
- Sovereignty issues regarding resource access.
- Potential impacts on its blue economy ambitions and fisheries sector.
- India’s hesitation may affect global acceptance and universal implementation of the treaty.
Conclusion
The UN High Seas Treaty represents a landmark in global ocean governance and marine conservation.
While India’s non-ratification poses a diplomatic challenge, the treaty offers an opportunity for nations to collaborate on:
- Protecting the common heritage of the high seas.
- Promoting sustainable development in international waters.
- Ensuring equitable access to marine resources.
India may need to balance national interests with global responsibilities as the treaty evolves.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- The UN High Seas Treaty is primarily concerned with:
A. Regulation of naval warfare
B. Conservation of marine biodiversity in national waters
C. Conservation of marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction
D. Combating piracy on the high seas
Answer: C. Conservation of marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction - The UN High Seas Treaty builds upon which of the following earlier international agreements?
A. Paris Agreement
B. Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
C. UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
D. Ramsar Convention
Answer: C. UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
Mains
1. The UN High Seas Treaty seeks to address regulatory gaps in ocean governance. Discuss its key provisions and significance. What are the possible reasons for India’s reluctance to ratify the treaty?
2. Critically examine how the UN High Seas Treaty can contribute to the achievement of SDG 14: Life Below Water.
7. Tourette Syndrome – Science and Technology
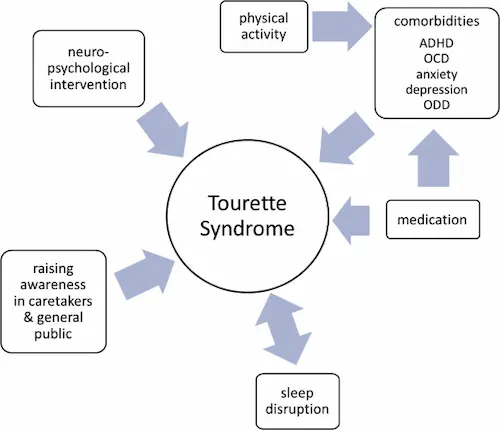
Why in News?
- Tourette Syndrome is a significant neurological disorder affecting individuals worldwide.
- Estimated global prevalence: 0.3% to 1%.
- There is growing awareness of its impact on daily functioning, communication, and mental health.
- The condition typically emerges in childhood and can significantly influence quality of life.
Key Points
1. What is Tourette Syndrome?
- A neurological disorder characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements and vocal sounds known as tics.
- Age of onset: Between 2 and 15 years (average ~6 years).
- Course:
- Symptoms often fluctuate in intensity.
- May improve with age in many individuals.
2. Types of Tics
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple motor tics | Single muscle group movements — e.g., eye blinking, shoulder shrugging. |
| Complex motor tics | Coordinated, purposeful-appearing movements — e.g., hopping, touching objects. |
| Simple vocal tics | Sounds like throat-clearing, grunting, sniffing. |
| Complex vocal tics | Words or phrases; in rare cases, coprolalia (uttering obscene words). |
Influence of Stress
- Stress, anxiety, and excitement typically worsen tics.
- Tics may decrease during periods of calm, focus, or relaxation.
3. Associated Conditions (Comorbidities)
Tourette syndrome rarely occurs in isolation. It is often associated with:
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
- OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder)
- Anxiety disorders
- Learning disabilities
4. Treatment and Management
| Approach | Goal |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Helps manage and reduce tic severity. |
| Behavioral therapies | Improve control and coping mechanisms. |
| Medications (for severe cases) | Used when tics cause significant impairment. |
| Education and Support | Critical for improving social acceptance and quality of life. |
- No cure currently exists, but symptom management can greatly improve well-being.
5. Societal Importance
- Understanding Tourette syndrome helps:
- Promote inclusion and empathy.
- Reduce stigma and misconceptions.
- Improve access to appropriate care and support systems.
- With suitable management, individuals with Tourette syndrome can lead fulfilling, productive lives.
Conclusion
Tourette Syndrome highlights the need for a holistic approach to healthcare — addressing not only physical symptoms but also psychological well-being, social support, and educational needs.
Ongoing research, public awareness, and inclusive healthcare policies can further improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Exam Connect – Possible Questions
Prelims
- Which of the following is a common characteristic of Tourette Syndrome?
A. Loss of muscle tone
B. Impaired cognitive ability
C. Involuntary motor and vocal tics
D.Progressive muscle paralysis
Answer: C. Involuntary motor and vocal tics - Coprolalia, sometimes observed in Tourette Syndrome, refers to:
A. Difficulty swallowing
B. Repetitive muscle spasms
C. The use of obscene language
D. Sleep disturbances
Answer: C. The use of obscene language
Mains
1. What is Tourette Syndrome? Discuss its impact on individuals and the role of public awareness and healthcare strategies in improving the quality of life for those affected.
2. Tourette Syndrome often coexists with other neuropsychiatric disorders. Explain the significance of an integrated treatment approach in managing such comorbidities.

